| Buzzoni, A., & Arnaboldi, M.: |
| "Planetary Nebulae as tracers of the Intergalactic stellar
background: a population synthesis theoretical approach", |
| 2004, ESO intl. Workshop on "Planetary Nebulae beyond the Milky Way",
Garching bei München (Germany), May 19-21, 2004 -
ESO Astrophysics Symposia, eds. L. Stanghellini, J.R. Walsh & N.G. Douglas,
(Springer Verlag: Heidelberg), p. 355.
|
| |
Unpublished data -
Set 1: PN lifetime and luminosity-specific PN density for SSP
synthesis models. ASCII data sources for Figs. 2 and 3.
Set 2: luminosity-specific PN density (in bolometric) for template galaxy models, according
to Buzzoni (2002). ASCII data sources for Fig. 4.
|
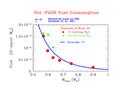 |
Figure 1 -
Theoretical fuel consumption for stars along the Hot-PAGB
evolution according to the models of Paczynski (1971; solid curve) and
Vassiliadis and Wood (1994; solid dots and triangles). Fuel is
expressed in Hydrogen-equivalent solar mass. The stellar core-mass
range to produce PNe is marked, after Dorman et al. (1993).
|
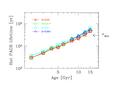 |
Figure 2 -
Hot-PAGB core mass lifetime, for SSP evolution according to
B89 synthesis models. A Salpeter IMF is assumed, and a Reimers mass
loss rate coefficient η = 0.3. The explored metallicity spans the
range from Z~1/20--2 Z(sun), as labeled in the plot.
The PN dynamical timescale [τ(dyn)] is also marked, for reference.
|
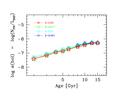 |
Figure 3 -
Theoretical luminosity-specific PN density for SSPs of
different metallicity. Models are according to Buzzoni (1989), with the distinctive
parameters as in Fig. 2. |
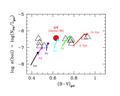 |
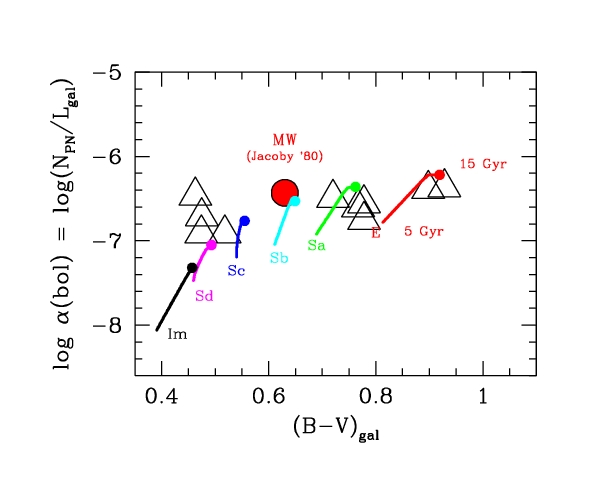
Figure 4 -
Expected luminosity-specific PN density for template galaxy
models (labeled with the corresponding Hubble type), according to
Buzzoni (2002). Each curve tracks galaxy evolution from 5 Gyr to 15
Gyr (small solid dots), as labeled for the case of Ellipticals. Big
triangles report the empirical estimate of α = N(PN)/L(gal)
from the PN census of Jacoby (1980) for the galaxies in the
Local Group. The case of the Milky Way is singled out in the plot by
the big solid dot.
|