

LBT Infrared Test Camera





The InfraRed Test Cameras (IRTC) are two technical imagers for the commissioning of the Adaptive Optics (AO) secondary mirror system and Gregorian foci of LBT.
The main top level requirements for the IRTC are as follows:
During the design phase, it was recognized that in the fine plate scale mode, the field of view imposed by the commercially available detectors was not sufficient to properly image the Point Spread Function (PSF) halo induced by the high-order modes of the adaptive secondary mirror. It was therefore decided to implement a third optical configuration, since the alternative solution of choosing a larger detector would have increased the cost to an unacceptable level. To summarize, the three optical configurations of the camera are:
The camera optical layout features three Calcium Fluoride lenses, to maximize the infrared transmission; the three optical configurations are obtained by moving two lenses along the optical axis, by mean of remotely controlled mechanisms. Two commercial filters are included in the design with band-passes 1050-1100 nm and 1500-1700nm (including the detector response cut-off at 1700nm). The two filters are mounted on a positioning system, which also includes a blank position. In order to minimize the stray light and the spurious background (non-thermal), baffles and pupil stops (one stop for each configuration) are included inside the camera.
In order to meet all the required functionalities, a total of four motorized functions are included in the camera design and an
anti-collision system is implemented. All motorized stages are off-the-shelf, while the mechanical structure of the camera, including optics mounts and interfaces to the telescope, are a custom design. The infrared camera is a commercial camera manufactured by Xenics, employing an InGaAs detector (320x256 pixels, 30 micron pitch) and equipped with a Peltier cooler and a liquid cooling system. All the other heat dissipating surfaces are chilled by a liquid cooling system, not to introduce any air turbulence especially in the critical regions inside the IRTC and in front of the AO wavefront sensor.
Dedicated custom software has been developed for motion control, optical configuration set-up, including filter exchange and pupil stops positioning, set-up of the infrared camera and image acquisition.
For further details on the LBT Infrared Test Camera please see: Foppiani
et al., "An Infrared Test Camera for LBT adaptive optics commissioning",
proc. SPIE 7015, pp. 701562-701562-11 (2008). The paper is available
here.
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers.
One print or electronic copy may be made for personal use only.
Systematic electronic or print reproduction and distribution,
duplication of any material in this paper for a fee or for commercial
purposes, or modification of the content of the paper are prohibited.
DOI.
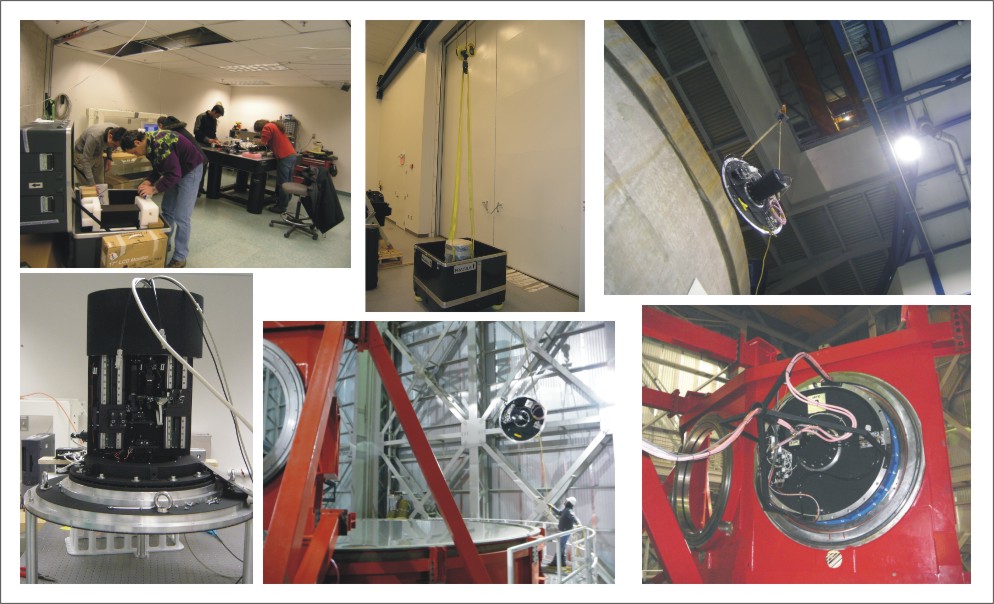
The IRTC project started officially in February 2007. A formal design review was passed in April 2007. The first IRTC was accepted in November 2007 and delivered to the Observatory of Arcetri in January 2008, to be used for the tests of the LBT AO system in the laboratory. The second IRTC passed the acceptance test in February 2008 and was installed at the LBT bent Gregorian focus in April 2008.
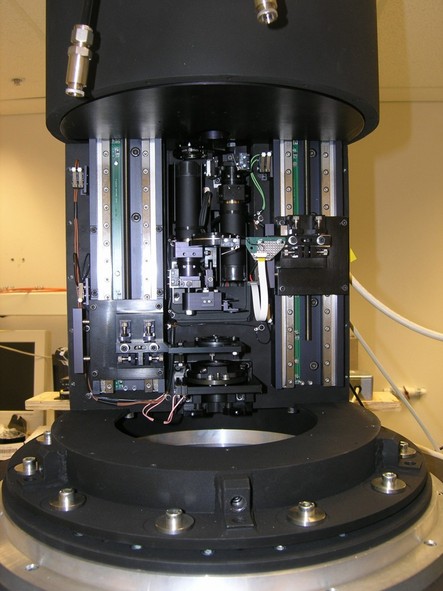
The IRTC has been designed and built by the following team:
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna
Alma Mater Studiorum Universita' di Bologna - Dipartimento di Astronomia
Max-Planck-Institut fuer Astronomie - Heidelberg